单链表
本文最后更新于:2022年12月13日 晚上
链表
基本介绍
链表是有序的列表,但是它在内存中是存储如下
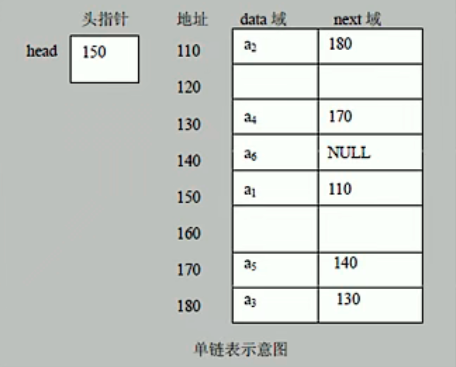
- 链表是以节点的方式来存储
- 每个节点包含data域, next域:指向下一个节点
- 如图:发现链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储
- 链表分带头节点的链表和没有头节点的链表,根据实际的需求来确定
单链表(带头结点)的逻辑结构
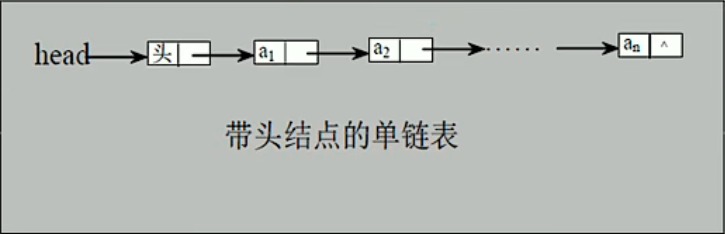
实现思路
添加(创建)
- 先创建一个head头节点,作用就是表示单链表的头
- 每添加一个节点,默认加入到链表的最后
- 如果要添加新节点newNode到指定位置,要创建辅助指针temp,通过遍历找到新添加的节点的位置,然后将
newNode.next = temp.next,将temp.next = newNode
遍历
通过一个辅助指针,辅助遍历整个链表
修改
先遍历链表,找到要修改的节点位置,用新节点的信息替换旧节点
删除
- 使用辅助指针temp,找到并指向需要删除的节点的前一个结点
temp.next = temp.next.next- 被删除的节点将不会有引用指向,会被垃圾回收机制回收
代码实现
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建节点
HeroNode hero_1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨");
HeroNode hero_2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义", "玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero_3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用", "智多星");
HeroNode hero_4 = new HeroNode(4, "公孙胜", "入云龙");
HeroNode hero_5 = new HeroNode(5, "林冲", "豹子头");
// 创建链表
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
// 加入
// singleLinkedList.add(hero_1);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero_2);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero_3);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero_4);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero_5);
// 按照编号顺序添加
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero_1);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero_4);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero_3);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero_2);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero_5);
System.out.println("原始链表");
singleLinkedList.list();
singleLinkedList.update(new HeroNode(5, "林冲u", "豹子头u"));
singleLinkedList.update(new HeroNode(6, "林冲u", "豹子头u"));
// 输出链表
System.out.println("修改后链表");
singleLinkedList.list();
singleLinkedList.del(5);
singleLinkedList.del(2);
singleLinkedList.del(1);
System.out.println("删除后链表");
singleLinkedList.list();
}
}
// 定义SingleLinkedList 管理英雄
class SingleLinkedList {
// 初始化一个头节点
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
// 添加节点到单向链表
// 1. 找到当前链表的最后节点
// 2. 将最后这个节点的next指向新的节点
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 因为 head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助变量 temp
HeroNode temp = head;
// 遍历链表,找的最后节点
while (true) {
// 找到链表的最后
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// 没有找到最后,将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
// 当退出while循环时,temp就指向链表最后
temp.next = heroNode;
}
// 第二种方式在添加英雄时,根据排名将英雄插入到指定位置
// (如果有这个排名,则添加失败,并给出提示)
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 因为 head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助变量 temp
// 因为单链表,因为我们找的temp是位于添加位置的前一个节点,否则插入不了
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false; // 标志添加的编号是否存在,默认为false
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {
// 位置找到,就在temp的后面插入
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
// 说明希望添加的heroNode的编号已然存在
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next; // 后移,遍历当前链表
}
// 判断flag的值
if (flag) {
// 不能添加,说明编号已存在
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄编号 %d 已经存在了,不能加入\n", heroNode.no);
} else {
// 插入链表中,temp的后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
// 根据no编号修改节点信息
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) {
// 判断是否为空
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 根据no编号找到需要修改的节点
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false; // 表示是否找到该节点
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
break; // 链表遍历完毕
}
if (temp.no == newHeroNode.no) {
// 找到
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag) {
// 找到
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickName = newHeroNode.nickName;
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为 %d 的节点\n", newHeroNode.no);
}
}
//删除指定节点
public void del(int no) {
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false; // 标志是否找到代删除的节点
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == no) {
//找到了待删除节点的前一个节点
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
} else {
System.out.printf("待删除的节点 %d 不存在\n", no);
}
}
// 遍历链表
public void list() {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 因为 head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助变量 temp
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
// 判断是否到链表最后
if (temp == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
// 定义HeroNode,每个HeroNode 对象就是一个节点
class HeroNode {
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickName;
public HeroNode next; // 指向下一个节点
// 构造器
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickName) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickName = nickName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickName='" + nickName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
相关题目:
求单链表有效节点数
思路:遍历当前链表,length++
代码:
// 输出有效节点数
public int getLength() {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
HeroNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return length;
}测试:
System.out.println("有效节点长度为 " + singleLinkedList.getLength()); // 5查找单链表中的倒数第k个节点
思路:
- 求出链表总长度
size - 倒数第k个节点就为正数第
size-k+1个节点
代码:
// 查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点
public HeroNode findLastIndexNode(int index) {
// 判断非空
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
// 第一次遍历得到链表的节点个数
int size = this.getLength();
// 第二次遍历,首先判断 index 合法性
if (index <= 0 || index > size) {
System.out.println("index不合法");
return null;
}
// 定义一个辅助变量,通过for 循环到达指定位置
HeroNode cur = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}测试:
System.out.println(singleLinkedList.findLastIndexNode(3));反转链表
思路:
- 先定义一个节点reverseHead
- 从头到尾遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reverseHead的最前端,原来的链表的
head.next =reverseHead.next
代码:
// 反转单链表
public void reverseList() {
// 若当前链表为空或者只有一个节点则无需反转
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
System.out.println("当前链表为空或者只有一个节点,无需反转");
return;
}
// 定义一个辅助的指针(变量),帮助我们遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur = head.next;
HeroNode next = null; // 指向当前节点的[cur]的下一个节点
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
// 遍历原来的链表
// 每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表 reverseHead 的最前端
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next; // 先暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点
cur.next = reverseHead.next; // 将cur的下一个节点指向新的链表的头部
reverseHead.next = cur;
cur = next; // 让cur后移
}
// 换
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}逆序打印单链表
思路:
- 先反转单链表,再遍历打印(破坏原始单链表的结构,不建议)
- 将每个节点压入到栈中,利用栈先进后出的特点实现逆序打印
代码:
public void reversePrint() {
if (head.next == null) {
return; // 空链表,不能打印
}
// 创建栈,
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
HeroNode cur = head.next;
// 将各个节点压入栈中
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur); // 压入栈中
cur = cur.next;
}
// 将栈中的节点进行打印,出栈
while (stack.size() > 0) {
System.out.println(stack.pop()); //
}
}合并两个有序的链表
方法一 使用递归
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}else if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}else if(list1.val >= list2.val){
list2.next =
mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}else{
list1.next =
mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
}
}方法二
删除排序链表中的重复元素
初解思路
双循环,双指针,新建辅助指针temp循环遍历,再建立辅助指针cur,初始指向temp.next,循环与temp比较值,相等是让temp.next = cur.next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
// 让temp指向头节点
ListNode temp = head;
// 循环
while(true){
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
ListNode cur = temp.next;
boolean flag = false; // 标记cur是否指向末尾
while(true){
if(temp.val == cur.val){
temp.next = cur.next;
}else{
break;
}
// 此条件要退出两个循环
if(cur.next == null){
flag = true;
break;
}
// 此条件只退出一个循环
if(cur.next.val > temp.val){
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 判断cur是否指向末尾
if(flag){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
}优化解法
单指针,单循环,用temp和temp.next比较,如果相等则让temp.next = temp.next.next,不相等则让temp = temp.next
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
// 让temp指向头节点
ListNode temp = head;
// 循环
while(temp.next != null){
if(temp.next.val == temp.val){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
// 如果下面用else,下面这个判断就不用写了
if(temp.next == null){
break;
}
}
// 这里绕弯子了,直接else就行
if(temp.next.val > temp.val){
temp = temp.next;
}
}
return head;
}终极解法
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
// 让temp指向头节点
ListNode temp = head;
// 循环
while(temp.next != null){
if(temp.next.val == temp.val){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else{
temp = temp.next;
}
}
return head;
}相交链表
思路分析
我的解法:双指针,等于则return
官方的第二种解法很妙
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 过滤空链表情况
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
ListNode temp1 = headA;
ListNode temp2 = headB;
while(temp1 != null){
temp2 = headB;
while(temp2 != null){
if(temp1 == temp2){
return temp1;
}
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp1 = temp1.next;
}
return null;
}
}官方解法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}环形链表
可以直接用哈希表秒杀,快慢指针法有意思!
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}单链表
https://yorick-ryu.github.io/数据结构/数据结构_单链表/